What is Internet of Things?
Why is IoT so important?
Over the past few years, IoT has become one of the most important technologies of the 21st century. Now that we can connect everyday objects like kitchen appliances, cars, thermostats, baby monitors to the internet via embedded devices, seamless communication is possible between people, processes, and things.
By means of low-cost computing, the cloud, big data, analytics, and mobile technologies, physical things can share and collect data with minimal human intervention. In this hyperconnected world, digital systems can record, monitor, and adjust each interaction between connected things. The physical world meets the digital world and they cooperate.
How does IoT work?
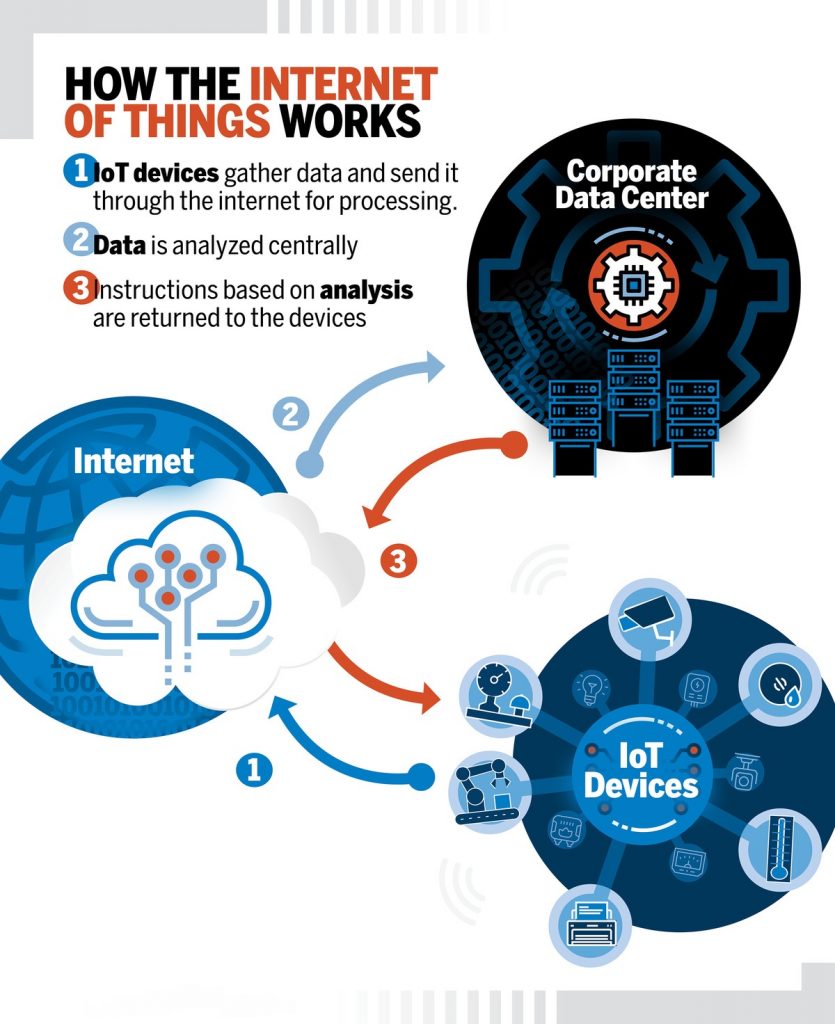
An IoT ecosystem consists of web-enabled smart devices that use embedded systems, such as processors, sensors, and communication hardware, to collect, send and act on data they acquire from their environments. IoT devices share the sensor data they collect by connecting to an IoT gateway or other edge device where data is either sent to the cloud to be analyzed or analyzed locally. Sometimes, these devices communicate with other related devices and act on the information they get from one another. The devices do most of the work without human intervention, although people can interact with the devices — for instance, to set them up, give them instructions or access the data.
The connectivity, networking and communication protocols used with these web-enabled devices largely depend on the specific IoT applications deployed.
IoT can also make use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to aid in making data collecting processes easier and more dynamic.
What Technologies have made IoT possible?
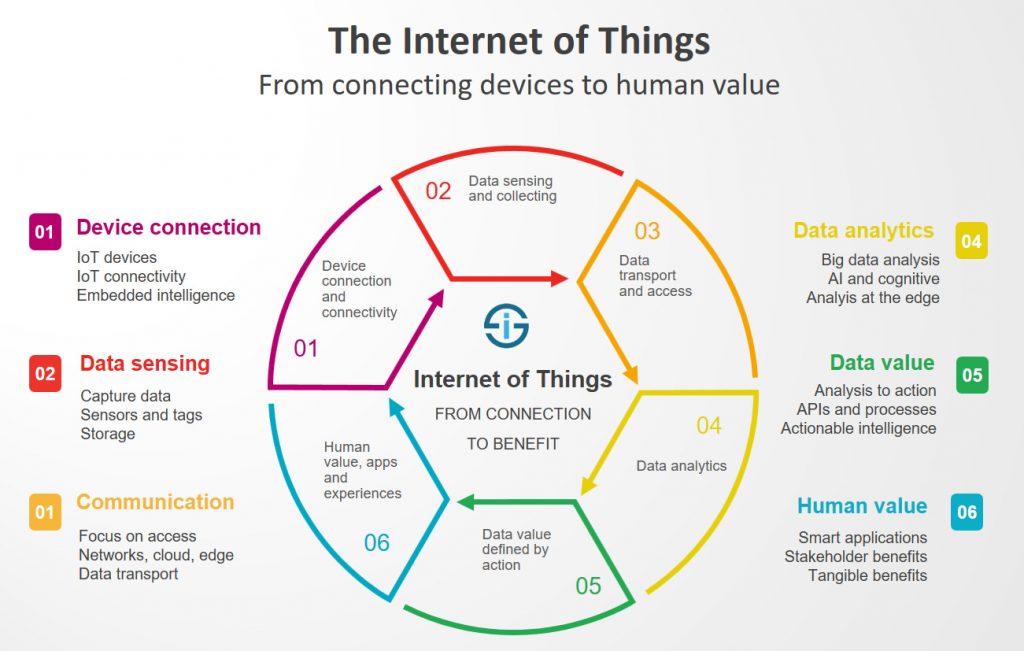
While the idea of IoT has been in existence for a long time, a collection of recent advances in a number of different technologies has made it practical.
- Access to low-cost, low-power sensor technology. Affordable and reliable sensors are making IoT technology possible for more manufacturers.
- Connectivity. A host of network protocols for the internet has made it easy to connect sensors to the cloud and to other “things” for efficient data transfer.
- Cloud computing platforms. The increase in the availability of cloud platforms enables both businesses and consumers to access the infrastructure they need to scale up without actually having to manage it all.
- Machine learning and analytics. With advances in machine learning and analytics, along with access to varied and vast amounts of data stored in the cloud, businesses can gather insights faster and more easily. The emergence of these allied technologies continues to push the boundaries of IoT and the data produced by IoT also feeds these technologies.
- Conversational artificial intelligence (AI). Advances in neural networks have brought natural-language processing (NLP) to IoT devices (such as digital personal assistants Alexa, Cortana, and Siri) and made them appealing, affordable, and viable for home use.
What industries can benefit from IoT?
- Manufacturing
- Automotive
- Transportation and Logistics
- Retail
- Public Sector
- Healthcare
- General Safety Across All Industries
Pros and Cons of IoT
Some of the advantages of IoT include the following:
- Ability to access information from anywhere at any time on any device.
- Improved communication between connected electronic devices.
- Transferring data packets over a connected network saves time and money.
- Automating tasks helps to improve the quality of a business’s services and reduces the need for human intervention.
Some disadvantages of IoT include the following:
- As the number of connected devices increases and more information is shared between devices, the potential that a hacker could steal confidential information also increases.
- Enterprises may eventually have to deal with massive numbers — maybe even millions — of IoT devices, and collecting and managing the data from all those devices will be challenging.
- If there’s a bug in the system, it’s likely that every connected device will become corrupted.
Since there’s no international standard of compatibility for IoT, it’s difficult for devices from different manufacturers to communicate with each other.